Schneider Electric Lighting protection
schneider lighting protection for low-voltage power and control
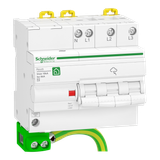
Projects that mix drives, LED lighting, and sensitive PLC I/O need predictable protection from switching spikes and atmospheric surges. Schneider’s portfolio covers service entrances, main distribution, sub-boards, and point-of-use circuits with coordinated stages, so let-through voltage stays below equipment impulse ratings. Modules are DIN 18-mm pitch with pluggable cartridges, visual/end-of-life flags, remote changeover contacts for BMS/SCADA, and thermal disconnectors that open safely under sustained overvoltage (TOV).
schneider surge protection devices classes and ratings
Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3 follow IEC 61643-11 and integrate cleanly with Acti9/Multi9 rails and Prisma boards.
- Type 1 (spark-gap or hybrid) for origin of installation—tested with the 10/350 µs waveform. Typical Iimp 12.5 kA per pole (25 kA options for high keraunic zones). Low follow current keeps upstream breakers from nuisance tripping on TN-C/TN-S.
- Type 2 (MOV or hybrid) for main and sub distribution—8/20 µs class with In 20…40 kA and Imax 40…80 kA, Up commonly 1.2…1.5 kV on 230/400 V systems. These take the bulk of switching surges from VFDs and large contactors.
- Type 3 at the equipment inlet—plug/socket or DIN auxiliaries that clamp the residual to electronics-safe levels next to LED drivers, power supplies, and control gear.
Common Uc values: 255/275 V (L-N), 320 V where permanent overvoltage risk exists, and 255/275/440 V on N-PE/L-PE paths depending on system earthing (TT, TN, IT). Response is in the nanoseconds for MOV stages; coordinated spark gaps handle high-energy impulses without high let-through.
Product range and series overview for panel builders
- Service entrance kits with Type 1 arresters and upstream gG/MCCB coordination data; options for N-PE spark gap on TT networks.
- Distribution-board cartridges (single or three-phase + N) with replaceable MOV blocks, mechanical lockout during replacement, and front test/access windows.
- Point-of-use protectors for luminaires, signage, and control power, including compact DIN blocks that sit next to 24 V SMPS and PLC racks.
- Signaling and accessories: remote dry contact (changeover), busbar adapters, phase barriers, and pre-wired link kits that reduce wiring time in dense boards.
These schneider SPD modules keep the mechanical language consistent—same terminal geometry, same torque values, and the same 18-mm pitch across protection tiers.
System architecture and coordination rules
Stage SPDs as a three-level scheme: Type 1 at the service, Type 2 at distribution/MCC, Type 3 at sensitive loads. Maintain cable lengths as short as possible—aim for ≤0.5 m from phase to SPD to PE and the same back to the bus; if the run can’t be shortened, use a V-connection to limit inductive overshoot. Coordinate upstream protection: many frames allow back-up with 125 A gG/gL fuses or specified MCB curves so the SPD isn’t cleared before it has done its work. On TT systems, bond the N-PE path with a dedicated spark-gap element to avoid steady leakage. For IT, select L-L modes and confirm insulation monitoring device behavior during surge events.
schneider lightning arresters for service entrances
Where the site has external LPS or high strike density, choose Type 1 spark-gap arresters at the origin. Iimp 12.5 kA per pole is standard; move to 25 kA where down-conductors terminate nearby or roof structures are expansive. Use four-pole sets on 3P+N, and land the PE tail directly to the main earthing bar—not via the breaker chassis. Keep the equipotential bonding conductors short and avoid sharp bends; the goal is low inductance so the first microseconds don’t create damaging potential rise across the board.
Technical specifications and standards
Conformity: IEC/EN 61643-11 (low-voltage SPDs), IEC 60364-5-53 (selection and erection), IEC 61000-4-5 (test surge immunity). Markings include Uc (max continuous operating voltage), In/Imax or Iimp, Up (voltage protection level), TOV withstand with time class, and short-circuit withstand with specified upstream device. Cartridges are hot-swappable after de-energizing and verifying isolation; status flags indicate “OK”, “Replace”, and some families add “End-of-life—disconnected”. Remote contacts signal maintenance needs to PLC/BMS. Typical wiring: 16–35 mm² on power paths, 6–16 mm² on PE tails depending on frame.
Applications and placement guidance
- Drives and robotics: Type 2 at the MCC feeding VFDs; Type 3 at the 24 V DC PSU for PLC and safety relays to keep logic rails clean.
- LED lighting and signage: Type 2 at the lighting board, then a compact point-of-use SPD near drivers to prevent nuisance dimmer failures.
- Process and utilities: Type 1 at incomer with TT or TN earthing, coordinated Type 2 on sub-boards that see long cable runs and outdoor lines.
- Building services: elevators, HVAC, and BMS panels benefit from coordinated stages; Up values below controller surge ratings prevent warranty pain.
Integration with Schneider platforms
SPDs mount beside Acti9 breakers and RCCBs; shunt-trip and undervoltage releases can be driven from SPD alarm contacts to shed nonessential feeders on severe events. With Compact NSX upstream, use Schneider selectivity/cascading tables so fault energy and follow current stay within device limits. Prisma/Spacial boards accept the same busbar accessories, which keeps assembly repeatable across board sizes and regions.
Selection criteria for B2B engineers
Define network and earthing (TT/TN/IT) first, then set Uc so TOV immunity matches local grid behavior. Choose Type 1 where external LPS or overhead lines exist; otherwise Type 2 at distribution plus Type 3 at sensitive loads. Size In/Imax or Iimp to the site’s keraunic level and cable lengths; target Up below equipment impulse capability (often 1.5 kV for electronics on 230/400 V). Confirm backup protection and short-circuit withstand; document tail lengths and routing on the drawing. For remote maintenance, wire the alarm contact into SCADA so teams see “replace cartridge” before failure. In specs and labels, call this layer schneider overvoltage protection so purchasing ties it to the correct family.
Procurement and kitting notes
Standardize one Type 1 frame for incomers, one Type 2 rating for sub-boards, and one point-of-use module for control/lighting. Pre-kit tails, lugs, phase barriers, and labels with each SPD so the fitter doesn’t chase parts. Include a spare cartridge per board in the site kit. Where outdoor runs are long, add equipotential bonding braid and gland EMC clamps to the same purchase line—those details make schneider transient suppressors effective in real cabinets, not just on paper.
Advantages of working with Bankoflamps
Bankoflamps ties pricing to your one-line and shows real-time EU stock before you lock schedules. Quotes usually land around the one-hour mark. Ordering by EAN/MPN prevents variant drift; the portal exposes lead times, shipment status, and downloadable price lists. Approved partners can use post-payment up to 30 days. We consolidate partials to cut freight and maintain price-validity windows so phased rollouts stay predictable. Your account manager cross-checks earthing scheme, Uc/Iimp/In, backup protection, and tail kits against your drawings so pallets arrive rail-ready—no missing links on site.