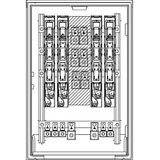
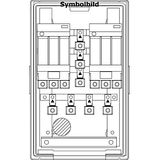
SCHRACK Electric box (breaker panel)
schrack distribution boards configuration, ratings, and form factors
Built for LV assemblies in commercial and light-industrial sites, these steel boards deliver modular DIN real estate on 18-mm pitch with standardized rail spacing and depth for auxiliaries. Typical incomers: 125–250 A (single row/mid boards) and up to 400–630 A on larger cabinets with split busbars. Prospective short-circuit ratings are specified per kit (commonly 6–10 kA at 230/400 V for modular tiers; higher with MCCB incomers). Protection classes IP30…IP55 (IK07…IK10) cover corridors to plant rooms; doors are RAL 7035 powder-coated steel with 120°–140° hinges and DIN-cut aperture options for meters/HHUs. Compliance: EN 61439-1/-2 (assemblies) and EN 61439-3 where apartment/utility boards apply.
Schrack Enclosures mechanical platform and accessories
Bodies are 1.0–1.5 mm zinc-plated, powder-coated steel; stainless variants are available for harsher rooms. Depths 150–250 mm with raised door options preserve wiring space over bulky RCBOs and AFDDs. Mounting plates, sliding DIN carriages, and height-adjustable chassis simplify mixed device heights. Cable entries use removable gland plates (top/bottom); knockouts are backed by protective edge guards. Options include transparent doors, key/quarter-turn locks, pressure equalizers, anti-condensation heaters, and labelled PE/MET bars.
schrack panel boards busbar systems and segregation
Comb busbars feed MCB/RCBO rows up to 125 A; fork/knife systems support higher density with reduced thermal hotspots. Split neutral bars and separate FE/PE bars keep metering and safety earth clean. Internal partitions and wire-duct dividers create power/drives/I/O lanes; shrouds and finger-safe barriers bring IP2X internal protection. Thermal spacers between rows are documented to maintain device derating at Ta 40 °C; optional plinths and rear spacers aid wall irregularities.
Product range and series overview for specifiers
- Flush/surface boards from 8 to ~72 modules; multi-row frames with shared door for risers and utility rooms.
- Metering cabinets with sealed CT chambers and MID meter apertures; service cut-out and MCCB incomer options.
- Main & sub-distribution cabinets with MCCB incomers, Type 2 SPD bays, and hinged chassis for live-front maintenance.
- IP55 service boards for plant corridors: gasketed doors, gland plates with drain geometry, and stainless hardware.
- Accessories: Type 1/2 SPDs, split load kits, inter-row links, blanking plates, DIN covers, cable retainers, door label frames, and hinged inner doors.
Technical specifications and standards engineers expect
- Assemblies: EN 61439 design verification (dielectric, temp-rise, short-circuit withstand, IP/IK).
- Protection devices: IEC/EN 60898-1 (MCB), 61009 (RCBO), 60947-2 (MCCB), 61643-11 (SPD).
- Creepage/clearance: maintained per device class; wiring to IEC 60204-1 principles for segregation.
- Earthing: TN-S/TN-C/TT layouts with labelled bars and removable links; PEN handling documented for local codes.
- Thermal management: perforated chassis, optional roof vents/filtered fans; published derating for clustered high-loss devices (AFDD, SPD, RCBO).
Applications and coordination
Office risers: stacked rows with selective RCDs upstream of 30 mA finals for discrimination. Retail: multi-row with metered sub-circuits and Type 2 SPDs at infeed. Light industry: MCCB incomer, RCBO finals, and motor feeders via contactor groups. Data/IT rooms: segregated essential/non-essential rails and separate UPS bypass. In residential blocks, compact kits fill the role usually associated with schrack consumer units, adding AFDDs where national regs require them.
System architecture, metering, and protection topology
Incomer + SPD at the top, then selective RCDs/RCBOs on finals. Maintain conductor routing: mains left, drives centre, low-level right from the gland plate through relief bars. Use V-connected SPD tails ≤0.5 m to reduce Up. Where fault levels exceed MCB capacity, apply cascading with MCCB incomers using vendor tables. Metering options include DIN energy meters (Modbus/230 V AC aux) or panel meters; CT kits mount on split chassis with shielded secondaries routed away from high-dv/dt paths.
Integration with other ecosystems
Boards accept AFDDs, EV charge feeders, DALI lighting controllers, and BMS gateways on the same rails. Door hardware aligns with pilot devices and door-coupled isolators. For PLC/IIoT drops, DIN PSU and gateways mount on segregated rows with dedicated FE to reduce EMC issues. This mechanical and electrical language makes them a clean host for mixed vendor control tiers as well as schrack modular switchgear assemblies in the same riser.
Installation practices that prevent callbacks
Reserve 20–30 % spare module space and 30 % wire-duct headroom. Label rows and device references to the schematic; print torque tables inside the door. Keep neutral bars mirrored to row order; avoid shared neutrals across RCD groups. Use stainless fixings in damp rooms; prime and seal any paint breaks at bonding points. Verify door swing and clearance before landing conduits; hinge-out chassis save hours during FAT.
Selection criteria for B2B teams
- Incoming kA and capacity: choose MCCB/RCBO frames and Icc per calculated fault level; validate cascading/selectivity.
- Ingress/impact: IP/IK by location; transparent doors only where glare and UV are acceptable.
- Metering/comms: MID billing vs operational; Modbus/BACnet gateways for dashboards.
- SPD/RCD policy: type and placement for discrimination; coordinate Up with downstream driver immunity.
- Space and service: module count, spare %, hinged chassis, and inner doors for live-front work.
- Cable management: gland plate size, relief bars, and depth for AFDD/RCBO tails.
Procurement and kitting for rollouts
Fix a repeatable kit per board size: enclosure/frame, incomer (MCCB/isolator), SPD set, RCD/RCBO rows with comb busbars, neutral/earth bars, labels, and gland plates. Add hinged inner doors, blanking plates, relief bars, and a door torque/row map. Pre-cut busbar tooth maps reduce assembly time; specify wire colours and ferrule sizes in the article list so site crews match drawings without rework.
Advantages of working with Bankoflamps
Bankoflamps aligns pricing to your one-line and schedule, shows real-time EU stock, and returns quotes fast—around the one-hour mark in typical cases. Ordering by EAN/MPN prevents variant drift; your portal provides lead-time, shipment status, and downloadable price lists. Approved partners may use post-payment up to 30 days. We consolidate partials to cut freight and hold price-validity windows so phased floors stay predictable. Our team cross-checks Icc, IP/IK, metering, SPD/RCD policy, and chassis options against your drawings so pallets arrive complete—rail-ready from day one.